Together with DNA and proteins, RNA forms the trinity of macromolecules (large and heavy molecules) essential to all forms of life on earth. Many viruses have RNA as genetic material rather than DNA.
Together with DNA and proteins, RNA forms the trinity of macromolecules (large and heavy molecules) essential to all forms of life on earth. Many viruses have RNA as genetic material rather than DNA.
RNA versus DNA
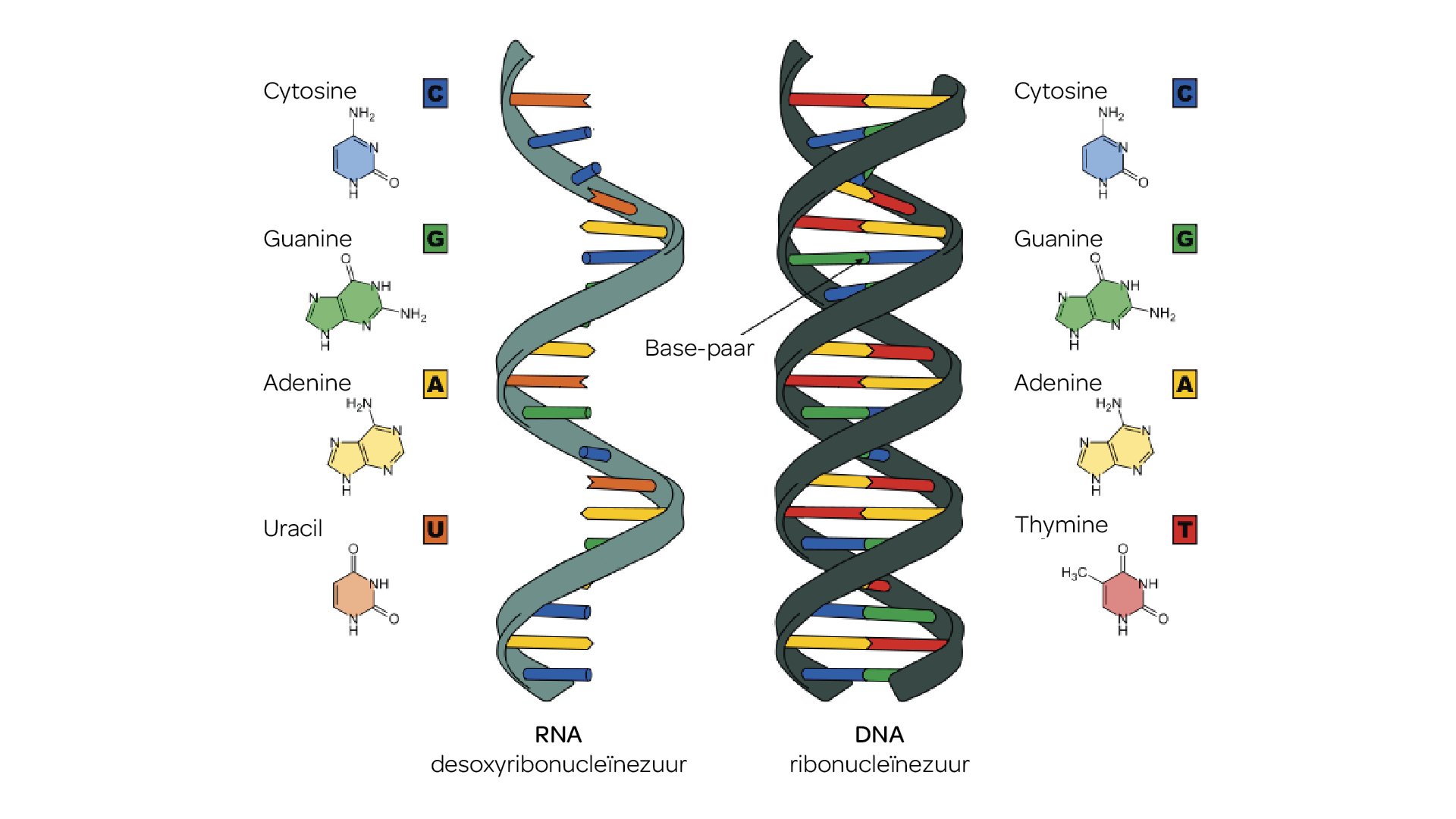
RNA is the abbreviation for ribonucleic acid. It is very similar to DNA. A RNA chain is constructed of four different nucleotides or building blocks just as is DNA. Both RNA and DNA are made up of adenine (A), cytosine (C) and guanine (G), but RNA has the nucleotide uracil (U), where DNA has thymine (T).
Transcript and translate
RNA is made when protein has to be produced in a cell. These proteins are needed for the cell to function. The synthesis of protein follows a number of steps:
- The DNA is read and copied. This copy comprises ‘messenger RNA’ (mRNA). This process is termed transcription.
- The mRNA chain is then translated into a protein. Every three nucleotides to be read have one amino acid linked to them. This process is termed translation.
- A series of amino acids is created in this way which are combined to produce the protein.